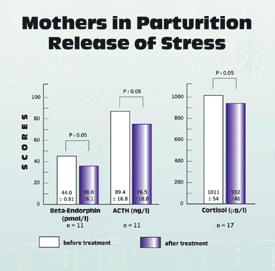
This is even more so the case when complications arise as in the investigated women here who showed an initial inactivity of the uterus. Seen from the angle of the hormone state the organism is in a state of emergency: to counteract the experience of great pain and severe stress for the mother, the organism produces 8-10 times more opioids as normal, which – next to other effects – function as anxiety inhibitors.
To find out in how far Medical Resonance Therapy Music® has a harmonizing effect on anxiety regulating neuroendocrine functions important opioids were chosen for investigation: beta-endorphin, corticotropin (ACTH) and cortisol – hormones which show extremely high levels in blood during labor.
Under investigation were three groups:
- one group (11 women) was treated with relaxing Medical Resonance Therapy Music®,
- a control group A (11 women) listened to music of Mozart – Symphony No. 28 and Coronation Mass – and
- a control group B (11 women) did not listen to any music.
Medical Resonance Therapy Music®
Group
The treatment with the Medical Resonance Therapy Music® resulted in a significant change of the hormonal situation:
the beta-endorphin value dropped by 6.05 units and also ACTH showed a tendency to decrease – the hyperproductive hormone system was calmed and a more balanced state established.
Especially noteworthy is the following situation: although the level of anxiety inhibiting hormones decreased the women did not experience a raise in anxiety but on the contrary reported of a clear decrease of anxiety.
This implies that the reduction of anxiety under the treatment with Medical Resonance Therapy Music® is based on a strong harmonizing effect on the emotional state during labor.
Control Group A with Mozart’s MusicThe treatment with the Medical Resonance Therapy Music® resulted in a significant change of the hormonal situation:
the beta-endorphin value dropped by 6.05 units and also ACTH showed a tendency to decrease – the hyperproductive hormone system was calmed and a more balanced state established.
Especially noteworthy is the following situation: although the level of anxiety inhibiting hormones decreased the women did not experience a raise in anxiety but on the contrary reported of a clear decrease of anxiety.
This implies that the reduction of anxiety under the treatment with Medical Resonance Therapy Music® is based on a strong harmonizing effect on the emotional state during labor.
The women in this group also reported of a strong reduction of anxiety through listening to the music. And here too a significant change was found in the hormonal situation, but in the opposite direction: the ACTH level increased – the already hyperactive hormone system got even more exaggerated and produced even more of the anxiety inhibiting hormone. The increase of the ACTH level could explain the reduced experience of anxiety in this group.
Control Group B
Here no significant changes were observed, only small variations.
Comments to Cortisol
A significant change of cortisol was neither found in the “Mozart group” nor in the Medical Resonance Therapy Music® group.
To get a reliable picture of the changes in cortisol level probably a longer than 30 minute treatment interval is necessary, since its duration is comparable with half the life span of the hormone in circulation.
Investigators:
Prof. Dr. med. A. Reznikov
Prof. Dr. med. S. Leush
Dr. med. V. Reznikov